Gum Therapy: Gum health is a crucial aspect of oral hygiene, yet it is often overlooked until problems arise. Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, affects millions of people worldwide and can lead to serious dental and overall health complications if left untreated. Understanding Gum Therapy options and preventive measures is essential for maintaining a healthy smile. This article delves into what gum Therapy involves, why it’s necessary, and how to prevent gum disease effectively.
What Is Gum Disease?
Gum disease is an infection of the tissues that support the teeth. It occurs when plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—builds up on the teeth and hardens into tartar, leading to inflammation of the gums. There are two main stages of gum disease:
- Gingivitis: This is the early stage of gum disease, characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. It is usually reversible with proper oral hygiene and professional cleaning.
- Periodontitis: If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease that damages the gums and bone supporting the teeth. This can lead to tooth loss if not properly managed.
Signs and Symptoms of Gum Disease
Recognizing the symptoms of gum disease early can help prevent complications. Common signs include:
- Swollen, red, or tender gums
- Bleeding while brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath (halitosis)
- Receding gums
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Pus around the gums
- Changes in bite alignment
Gum Therapy Options
Treatment for gum disease depends on the severity of the condition. Here are some common treatment methods:
1. Professional Dental Cleaning
For mild gum disease (gingivitis), a routine dental cleaning may be enough to remove plaque and tartar buildup. Dentists recommend professional cleanings at least twice a year to prevent gum disease.
2. Scaling and Root Planing
For more advanced gum disease, a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing is performed. This involves:
- Scaling: Removing plaque and tartar from the tooth surface and beneath the gums.
- Root Planing: Smoothing the root surfaces to prevent bacteria from reattaching and allowing the gums to heal.
3. Medications
In some cases, dentists may prescribe medications to control infection and inflammation, such as:
- Antibacterial mouthwashes
- Antibiotic gels applied to gum pockets
- Oral antibiotics
- Enzyme suppressants to slow down tissue destruction
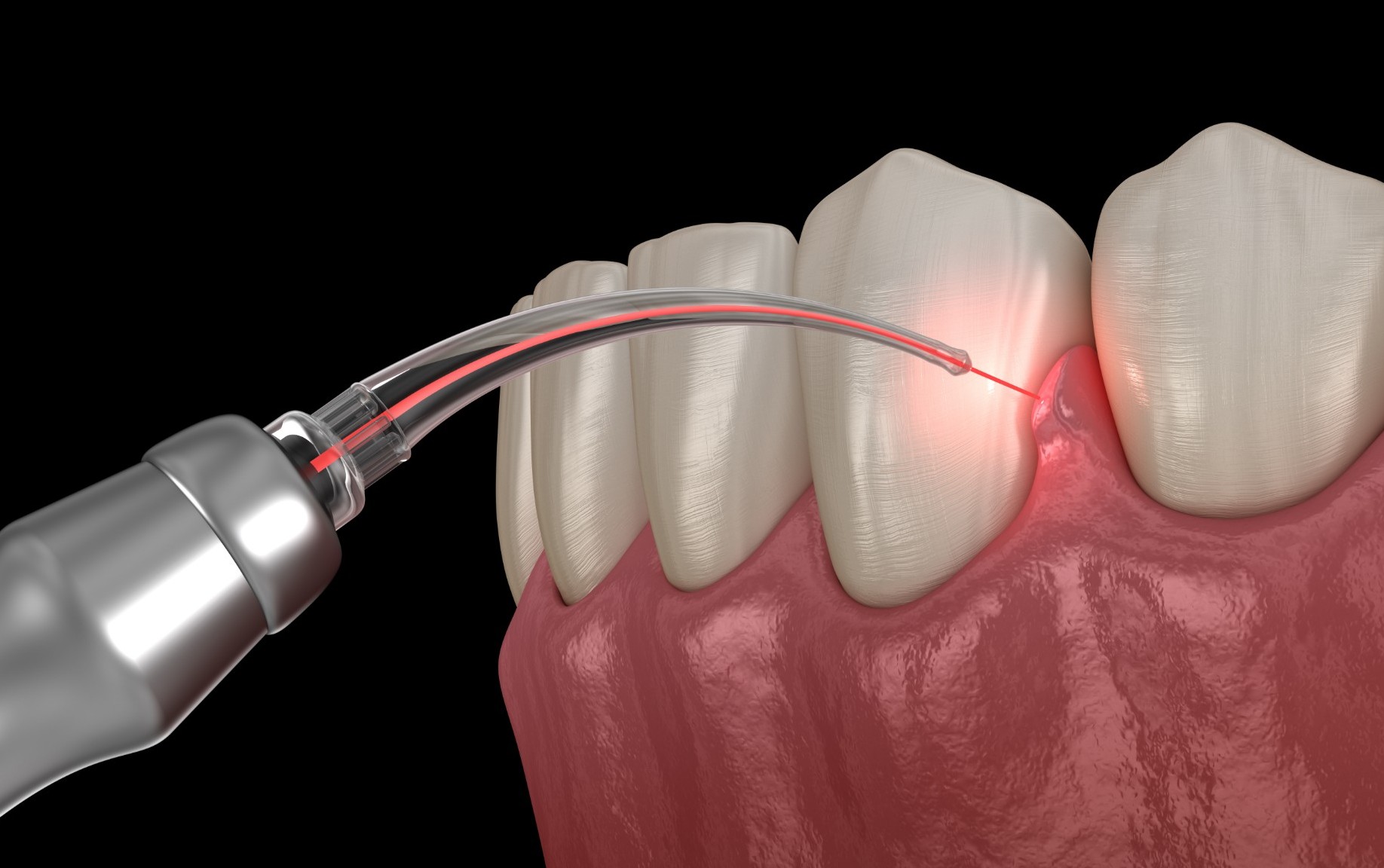
4. Laser Therapy
Laser treatment is a minimally invasive option that targets infected gum tissue and bacteria without causing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. It promotes faster healing and reduces discomfort compared to traditional methods.
5. Surgical Treatments
For severe periodontitis, surgical interventions may be necessary, including:
- Flap Surgery: The gums are lifted back for deep cleaning, then repositioned to reduce pocket depth.
- Gum Grafts: Tissue is taken from another part of the mouth to cover exposed roots and restore gum health.
- Bone Grafts: When bone loss has occurred, grafts help regenerate lost bone structure and support teeth.
Gum Therapy: Preventing Gum Disease
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are essential steps to maintain healthy gums:
1. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid damaging the gums.
- Floss daily to remove plaque from between teeth.
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce bacteria and freshen breath.
2. Visit Your Dentist Regularly
Regular dental check-ups and cleanings help detect and treat gum issues early. Most dentists recommend visiting at least twice a year, but more frequent visits may be needed for those with a history of gum disease.
3. Quit Smoking
Smoking is one of the biggest risk factors for gum disease. It weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight infections and heal damaged gums.
4. Eat a Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports gum health. Foods that promote strong gums include:
- Fruits and vegetables (high in vitamin C and antioxidants)
- Dairy products (rich in calcium)
- Nuts and seeds (contain essential nutrients for gum health)
- Green tea (has anti-inflammatory properties)
5. Manage Stress
Chronic stress can weaken the immune system and make the body more susceptible to infections, including gum disease. Practicing stress-reducing techniques like meditation, exercise, and adequate sleep can help maintain overall health.
Gum Therapy: Why Gum Health Matters
Gum disease is not just a dental issue—it can impact overall health. Research links periodontal disease to conditions like:
- Heart disease
- Diabetes
- Respiratory infections
- Pregnancy complications
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Maintaining healthy gums is essential for overall well-being, not just for preserving a beautiful smile.
Gum Therapy: Conclusion
Gum Therapy is essential for preventing and managing gum disease, which can lead to serious dental and health complications if ignored. From routine cleanings to advanced surgical procedures, there are many options available to restore and maintain gum health. By practicing good oral hygiene, visiting the dentist regularly, and making healthy lifestyle choices, you can keep your gums in optimal condition and avoid costly treatments in the future. Investing in gum health today will pay off in the long run with a healthier, brighter smile.
Finally, for more information about Gum Therapy cost and booking an appointment, here’s the link ; for before and after results, here’s our Instagram.